Frequently Asked Questions
What is critical communication and why is it important for professional users?
Critical communications include mobile, radio telecommunication systems and devices, and applications that must provide:
- Reliability
- Low latency & instantaneous communication
- Secure communications at all times
- Other special features
These systems are referred to as business -critical and mission -critical communication networks.
- Mission -critical networks are essential for the accomplishment of a specific mission. (For instance,transport, public safety, defence, disaster management, smart cities, etc.)
- Business-critical networks serve businesses that cannot operate without reliable communications for safety, efficiency and productivity (industries like manufacturing, utilities, oil and gas, mining and so on).
Mission-critical networks have been traditionally based on narrowband technologies such as TETRA, DMR, etc. However, there is an increasing need to evolve to broadband technologies, such as LTE 4G/5G.
What is broadband and how is it different from narrowband?
Broadband is the transmission of wide -bandwidth data over a wired/wireless network connection. Broadband connections include wireless technologies (such as LTE 4G/, 5G, Wi-Fi, etc.), wired technologies (such as fibre networks) and extra-terrestrial wireless technologies (satellites).
We can assume a broadband network where the download speed is 25 Mbps and above and the upload speed is 3 Mbps or more.
Narrowband communication uses lower bandwidth in contrast to broadband. Narrowband technologies typically support voice and narrow data bandwidth (Kbps).
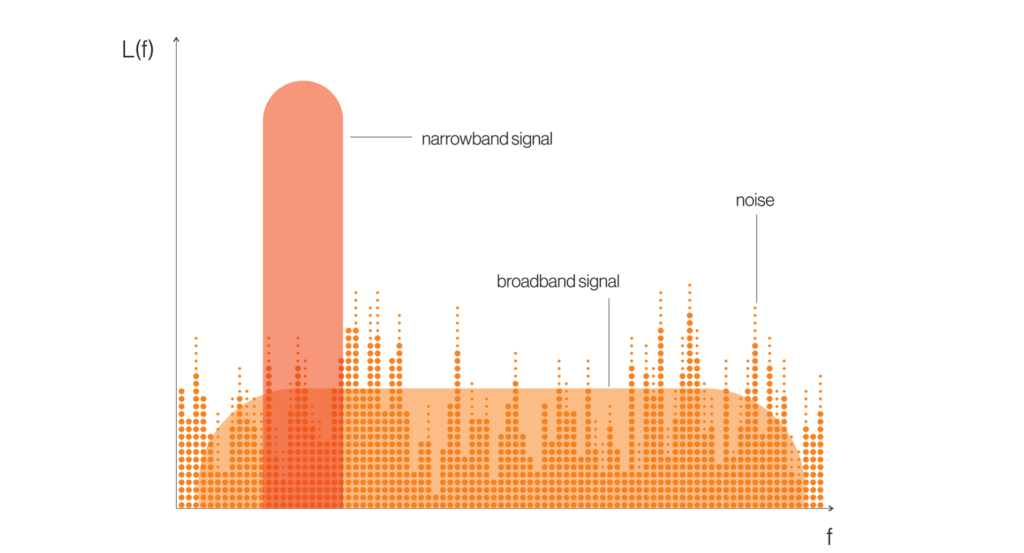
Narrowband communications have greater coverage and reliability in specific areas; for example, Push to Talk, critical alarms and location services work well with narrowband.
Applications using large volumes of data (e.g., video) do not work well on narrowband technologies; they require broadband. Mission -critical applications are increasingly adopting voice data and video, for which migration tobroadband technologies becomes imperative.
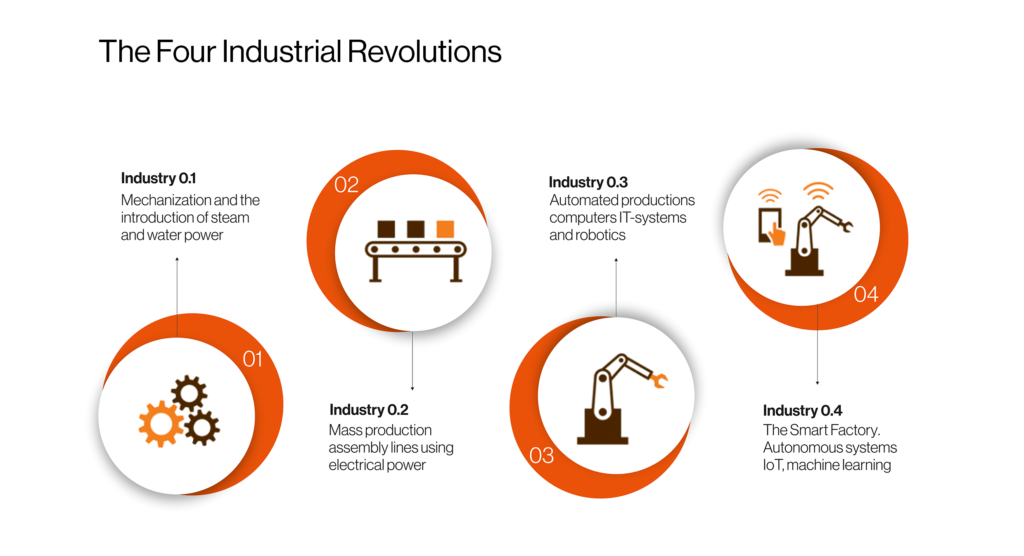
What is Industry 4.0? How is it achieved and what are its benefits?
Industry 4.0 is dramatically changing the way companies manufacture, refine and distribute their products. Companies are integrating and embracing new technologies, including cloud computing and analytics, Artificial Intelligence (Al) and Machine Learning (ML), Augmented Reality (AR), Mission Critical X (MCX) and the Internet of Things (IoT), into their production facilities and their operations.
How is Industry 4.0 achieved?
Private broadband networks, advanced sensors, embedded software in the new machines and robotics form the basis for Industry 4.0. The data from machines are being regularly collected, analysed and used for decision making, such as predictive maintenance, performance enhancement and process optimisation.
Technologies in Industry 4.0
The typical technologies adopted in this arena are private 4G/5G/Wi-Fi 6 networks, Cloud Computing, MCX (Mission-Critical X), IoT, AI and Machine Learning, and Cyber Security (Securing physical systems).
Benefits of Industry 4.0
Data being regularly captured and analyzed ensures the best use of technology with the following benefits.
- Predictive maintenance helps in decreasing equipment downtime.
- Increased automation results in lower costs, better efficiency and higher customer satisfaction.
- Self optimization for process improvements ensures continual refinements.
- Higher productivity
- Reduced manufacturing errors
What is Low Latency communication?
The term latency means delay. Low Latency Communication (LLC) describes a communication network optimised to process a very high volume of data messages with minimal delay. These networks are designed to support operations that require near real-time access to rapidly changing data. LLC are ultra-reliable and fast; they are essential for critical communication, in domains like manufacturing,transport, public safety, smart cities, etc. Current networks are capable of supporting a latency of 100-500 milliseconds.
Upcoming wireless technologies such as 5G deliver LLC, where data is transferred typically within less than ten milliseconds with high reliability.
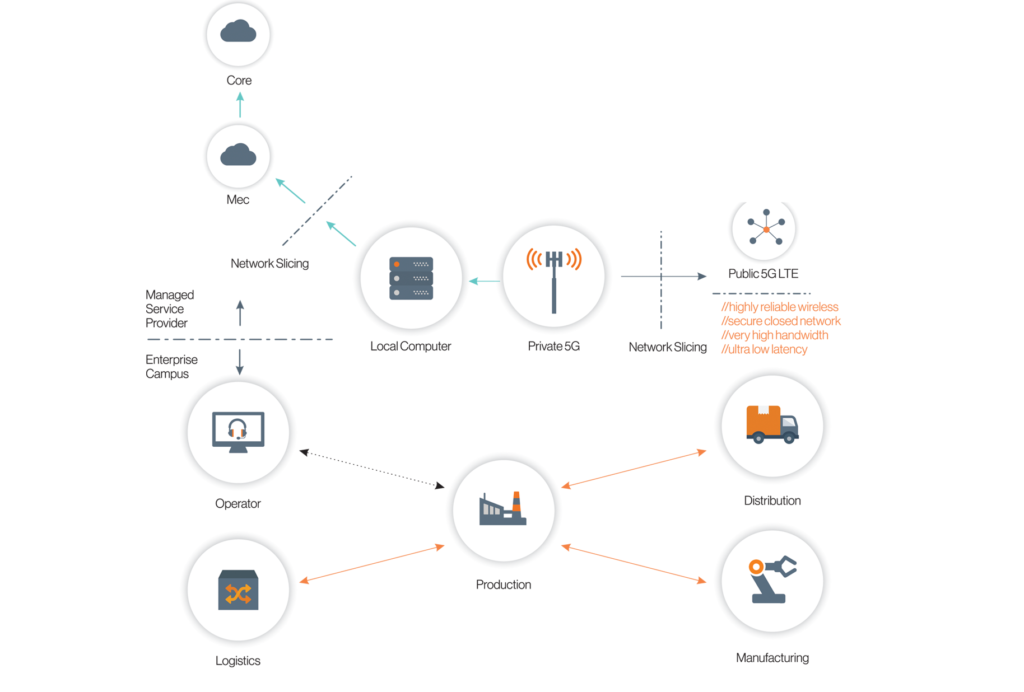
What is enterprise private LTE 4G/5G?
A private LTE 4G/5G network is a cellular network built specifically for an individual enterprise. Such networks find applications within a defined area; for example, in a factory, mine or campus.
Manufacturing, transport and public safety users are among the early adopters and beneficiaries of private LTE 4G/5G networks.
Why is LTE 4G/5G better than Wi-Fi?
5G is the umbrella term for fifth-generation cellular network technology, and it encompasses many different elements. Traditionally, cellular or mobile networks have relied on licensed spectrum bandsspectrum bands; however, due to the increasing adoption of LTE 4G/5G networks for private use, some spectrum is being made available on an unlicensed or privately licensed basis.
Wi-Fi relies on an unlicensed spectrum (range of frequencies) that’s free for anyone to use within a confined area. The range of Wi-Fi is usually within a few hundred meters from the transmission point; however, the range of a 4G/5G network can be many kilometers.
LTE 4G/5G technologies provide various features for mobile communications and are increasingly adding facilities required for mission -critical users; for instance, prioritisation of traffic. LTE 4G/5G networks also support higher mobility for users, a feature not supported by Wi-Fi technologies.
What can 4G/ 5G do for various industries?
The new 5G communication network enables highly reliable, secure and high-speed data transmission with short response times, making manufacturing more flexible, mobile and productive.
Why is it important to opt for telecom technologies that are OPEN global standards?
Industry standards refer to established technical specifications that a wide range of manufacturers can comply with, thereby increasing reliability, interoperability, efficiency and reducing cost across the supply chain of any industry. Standards drive innovation in an industry.
Standards like TETRA and, LTE 4G/5G evolved with a specific focus on standardisation and interoperability. At present, networks and devices from global manufacturers work seamlessly with each other.
What is MCX?
MCX is a new standard defined by ETSI and 3GPP, where X denotes several mission-critical (MC) services such as Push-To-Talk (PTT), Push-to-Data and Push-to-Video. MCX runs on LTE 4G/5G and future broadband systems.
In 2016, Mission -Critical Push-To-Talk (MCPTT) was introduced as an LTE feature in 3GPP Release 13 to address the needs of mission-critical communications. It has since then been enhanced to include data and video and has been rechristened as MCX (Mission-Critical X).
What are the benefits of MCX?
- Voice, Data and Video – Instantaneous group communication for voice, data and video. Provision to use broadband 3GPP as well as Non-3GPP Access Networks ensure support for new generation broadband applications.
- Low Latency and Prioritisation – MCX supports prioritisation of communication to across voice, data and video transmission. Advancements in 5G ensure low latency, which is vital for critical communication.
- Interoperable and Secure – MCX being part of the 3GPP standard evolution will ensure continuous enhancement and development. Interoperability will enable networks, application servers and user applications to work seamlessly with each other.
- Innovative Features – MCX supports a new generation of features required for critical communication applications, such as multi-device access, multi-user floor control, multi-ser- vice talk groups for PTT, Data and Video, and dynamic groups.
- Business Intelligence and Analytics – Next-generation applications enhance business intelligence and provide analytics required to enable Industry 4.0.
What will be the applications of MCX for critical communications?
MCX bases its architecture on broadband communication and provides innovative applications such as:
- Push to -To-X (Push-to -Talk, Data, Video)
- Integrated commandCommand and controlControl
- Advanced dispatching
- Integration with CCTV surveillance networks
- Integration with mass notification solutions
- Location tracking and routing applications
- Integration with sensors, loTs and alarm systems
- Analytics and rule-based alerts
How is MCX interoperable with narrowband systems?
MCX is interoperable with narrowband systems (TETRA, DMR, etc.) through a standard-based feature called the Inter Working Function (IWF). An IWF acts as a gateway to enable existing radio networks to connect and communicate with MCX services. Organisations would not have to replace their entire legacy infrastructure and systems (such as TETRA and DMR) while building out their broadband networks. Consequently, legacy networks can continue to co-exist with MCX services.
Can MCX be deployed over commercial networks?
Yes. MCX application services can be deployed over commercial LTE 4G/5G networks and can deliver very good, but best effort service levels. The networks can be upgraded to support features, such as prioritisation of traffic and expanding coverage to include all areas required for operation during normal and emergency situations.
What are the regulations around private LTE 4G/5G networks?
Regulations are crucial to organisations in deploying LTE 4G/5G networks. The technology is already available to allow for such deployments, ranging from small campuses/offices to large national networks.
While some countries already have regulations around such deployments, it is expected that all countries worldwide will allow private LTE 4G/5G network provisioning by 2025.
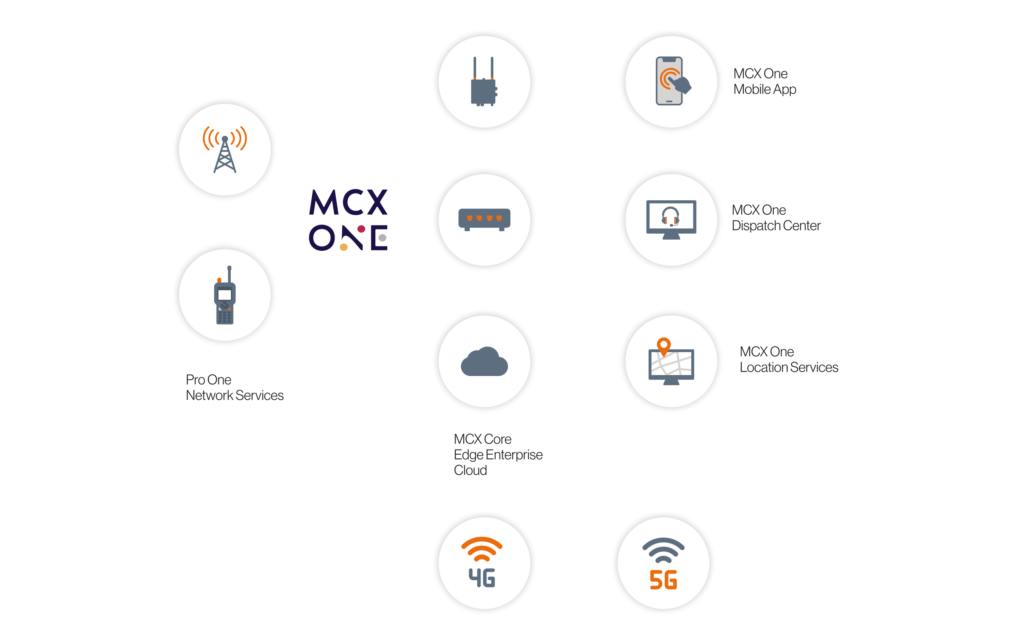
How can I upgrade my current PRO ONE network services with MCX?
Narrowband technologies (TETRA/DMR) are the preferred choices for critical communications today. Standardisation of MCX (Mission -Critical X) technology is leading the way for migration or co-deployment of broadband alongside existing networks. At present, most solutions are becoming increasingly hybrid installations, where TETRA, DMR run in parallel with LTE 4G and/Wi-Fi networks. With every new 3GPP release for mobile networks, the MCX standard is enhanced and will continue to deliver innovative applications.
Existing PRO ONE networks incorporate DAMM TetraFlex technology, which provides plug-and-play integration to PRO ONE NXT’S MCX ONE CORE solution.
PRO ONE NXT will therefore provide a future proof upgrade of narrowband to broadband critical communications.